
HEADACHE
Headache is among the most common reasons patients seek
medical attention and is responsible, on a global basis, for more
disability than any other neurologic problem.
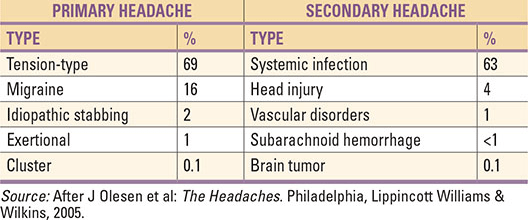
1. Tension-Type Headache (TTH)
Prevalence: Most common type (~42% lifetime prevalence).
Clinical features:
Bilateral, pressing or tightening (“band-like”) pain.
Mild to moderate intensity.
Not worsened by routine physical activity.
No nausea/vomiting (may have mild photophobia or phonophobia).
Triggers: Stress, poor posture, fatigue, anxiety.
Diagnosis: Based on history; normal neurological exam.
Treatment:
Acute: NSAIDs, paracetamol.
Preventive: Amitriptyline (if chronic), relaxation therapy, physiotherapy.
2. Migraine
Prevalence: ~15% of world population; women > men.
Types:
Migraine without aura (common migraine).
Migraine with aura (classic migraine) – transient neurological symptoms (visual: flashing lights, zig-zags; sensory: tingling).
Clinical features:
Recurrent attacks, 4–72 hrs.
Unilateral, throbbing/pulsating pain.
Moderate to severe intensity.
Associated with nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia.
Worsens with activity.
Triggers: Hormonal changes (menstruation), stress, lack of sleep, certain foods (cheese, chocolate, wine), weather changes.
Treatment:
Acute: Triptans (sumatriptan), NSAIDs.
Preventive: Beta-blockers (propranolol), Topiramate, Amitriptyline, CGRP monoclonal antibodies (erenumab).
Lifestyle: Sleep hygiene, trigger avoidance.
3. Cluster Headache (Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgia)
Prevalence: Rare (~0.1%); men > women.
Clinical features:
Excruciating, unilateral orbital/temporal pain.
Attacks last 15–180 minutes, 1–8 times/day, occurring in “clusters” over weeks.
Associated autonomic features: tearing, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, ptosis, miosis (Horner’s syndrome).
Restlessness/agitation (unlike migraine, where patients prefer lying still).
Triggers: Alcohol, strong odors, irregular sleep.
Treatment:
Acute: 100 % oxygen inhalation, subcutaneous sumatriptan.
Preventive: Verapamil (first-line), lithium, steroids for short-term prevention.
4. Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs)
Paroxysmal hemicrania: Severe unilateral headache, shorter than cluster (2–30 min), >5/day, responds dramatically to indomethacin.
SUNCT/SUNA: Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT) or autonomic symptoms (SUNA). Very rare.
5. Medication-Overuse Headache (MOH)
Cause: Regular overuse of analgesics, triptans, ergotamines (>10–15 days/month).
Clinical features:
Headache present on ≥15 days/month.
Daily or near-daily, worse on waking.
Improves temporarily after taking analgesics.
Management:
Withdrawal of overused medication (gradual or abrupt depending on drug).
Preventive therapy for primary headache (e.g., migraine prophylaxis).
6. Secondary Headaches (due to another disorder)
a) Vascular causes
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Sudden, “thunderclap” headache, worst in life, with neck stiffness, vomiting. Emergency CT/MRI.
Giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis): Age >50, temporal headache, scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, risk of blindness. High ESR/CRP. Treat with steroids.
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: Headache, seizures, focal deficits. MRI/MRV confirms.
b) Infectious causes
Meningitis/encephalitis: Fever, neck stiffness, photophobia, altered mental status.
Sinusitis: Frontal/maxillary pain, nasal discharge, worse on bending forward.
c) Trauma-related
Post-traumatic or post-concussion headache.
d) Neoplastic / raised intracranial pressure
Morning headache, vomiting, blurred vision, papilledema.
7. Other Specific Types
Cervicogenic headache: From neck disorders, radiates from occiput to front.
Trigeminal neuralgia: Brief, electric-shock-like unilateral facial pain triggered by touch/chewing.
Hormone-related headache: Menstrual migraine, pregnancy-associated.
Sleep-apnea headache: Morning headache, linked with obstructive sleep apnea.
📌 Key Takeaways
1. Primary headaches = Tension-type, Migraine, Cluster, other TACs.
2. Secondary headaches = Due to vascular, infection, trauma, tumor, drugs.
3. Red flags (SNOOP): Sudden, Neurological signs, Onset >50, Other systemic symptoms, Progressive.
4. Treatment depends on type: NSAIDs for TTH, triptans for migraine, oxygen for cluster, steroids for arteritis, antibiotics for meningitis.
5. Lifestyle management (sleep, hydration, stress reduction) is crucial in all types.

Warning: consultation should be done before taking any drugs given above every drug has benefits and side effect contact nearest physician, take care
Thankyou!!
